Introducing the diagram of soccer field with positions, a detailed guide that unravels the intricate world of soccer formations and player roles. This comprehensive resource delves into the standard dimensions, markings, and strategic positioning of players on the field, providing a deeper understanding of the game’s dynamics.
From the goalkeeper’s crucial role in defending the net to the specialized functions of defenders, midfielders, and forwards, this guide explores the responsibilities, movements, and skills required for each position. It also examines common formations, their advantages and disadvantages, and how they influence player positioning and team strategy.
1. Introduction
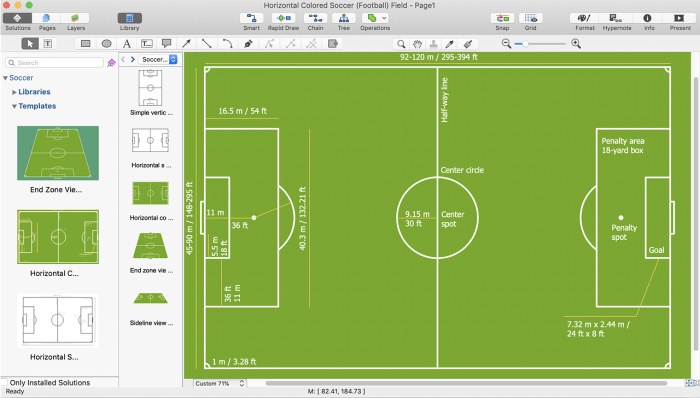
A soccer field diagram with player positions is a crucial tool for understanding the game’s tactics and strategies. It provides a visual representation of the field’s dimensions, markings, and the positioning of players during gameplay.
The standard soccer field is rectangular, with dimensions of 100-130 yards (90-120 meters) in length and 50-100 yards (45-90 meters) in width. The field is divided into two halves by a halfway line, and each half is further divided into two penalty areas and a goal area.
The goal is located at the center of each goal area.
2. Goalkeeper
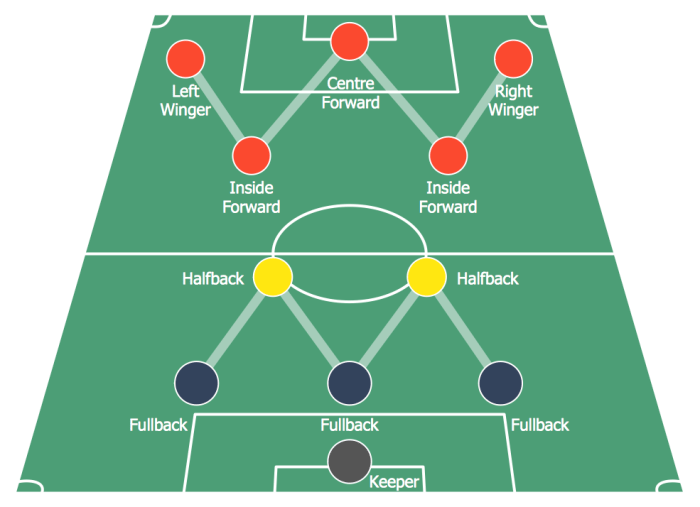
The goalkeeper is responsible for preventing the ball from entering the goal. They are the only players who are allowed to use their hands to handle the ball, but only within the penalty area.
Goalkeepers must be agile, have good reflexes, and be able to communicate effectively with their defenders. They must also be able to make quick decisions and distribute the ball effectively.
3. Defenders
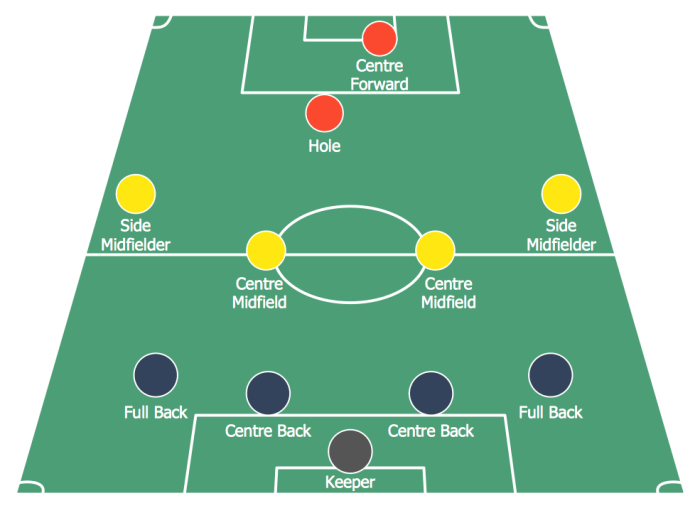
Defenders are responsible for preventing the opposition from scoring goals. They are typically positioned in front of the goalkeeper and behind the midfielders.
There are different types of defenders, including center-backs, full-backs, and wing-backs. Center-backs are responsible for marking opposition forwards and preventing them from getting into dangerous positions. Full-backs are responsible for marking opposition wingers and preventing them from crossing the ball into the penalty area.
Wing-backs are more attacking than full-backs and are often involved in the team’s attacking play.
4. Midfielders
Midfielders are responsible for linking the defense and attack. They are typically positioned between the defenders and forwards.
There are different types of midfielders, including central midfielders, attacking midfielders, and defensive midfielders. Central midfielders are responsible for controlling the tempo of the game and distributing the ball to the forwards. Attacking midfielders are responsible for creating chances for the forwards and scoring goals.
Defensive midfielders are responsible for protecting the defense and breaking up opposition attacks.
5. Forwards
Forwards are responsible for scoring goals. They are typically positioned in front of the midfielders and behind the defenders.
There are different types of forwards, including strikers, wingers, and target men. Strikers are responsible for scoring goals from close range. Wingers are responsible for providing width and crossing the ball into the penalty area. Target men are responsible for holding up the ball and bringing other players into the game.
6. Formations: Diagram Of Soccer Field With Positions
A soccer formation is a way of organizing players on the field. There are many different formations, but some of the most common include the 4-4-2, 3-5-2, and 4-3-3.
The 4-4-2 formation is a balanced formation that provides both defensive and attacking options. The 3-5-2 formation is a more attacking formation that gives the team more width and attacking options. The 4-3-3 formation is a more attacking formation that gives the team even more width and attacking options.
7. Tactics and Strategies
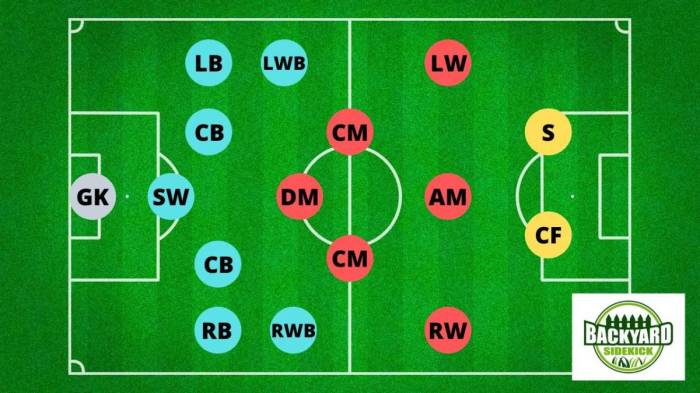
Soccer tactics and strategies are the ways in which a team organizes its players and plays the game. There are many different tactics and strategies, but some of the most common include possession-based play, counter-attacking, and long-ball play.
Possession-based play is a style of play that emphasizes keeping possession of the ball and creating chances through patient passing. Counter-attacking is a style of play that emphasizes winning the ball back quickly and attacking with speed and directness. Long-ball play is a style of play that emphasizes playing the ball long to forwards and target men.
8. Special Positions
In addition to the traditional positions, there are also a number of special positions that can be used in soccer. These positions include the libero, sweeper, and holding midfielder.
The libero is a defender who is given the freedom to roam behind the back four and cover for any gaps in the defense. The sweeper is a defender who is positioned behind the back four and is responsible for clearing any balls that get past the other defenders.
The holding midfielder is a midfielder who is positioned in front of the back four and is responsible for protecting the defense and breaking up opposition attacks.
Key Questions Answered
What are the standard dimensions of a soccer field?
The standard dimensions for a soccer field are 100-130 yards long and 50-100 yards wide.
What is the role of a libero in soccer?
A libero is a specialized defender who plays behind the back line, providing cover and sweeping up any loose balls.
How do formations influence player positioning?
Formations determine the starting positions and general areas of responsibility for each player on the field, influencing their movements and interactions.