Embark on an intellectual odyssey with our Evolution and Natural Selection Worksheet, a comprehensive guide that unveils the intricate mechanisms driving the diversity of life on Earth. Delve into the captivating world of evolution and natural selection, where the interplay of genetic variation, environmental pressures, and time shapes the tapestry of life.
Through this worksheet, you will unravel the compelling evidence supporting evolution, from the fossil record to comparative anatomy and molecular biology. Engage in critical thinking as we address common misconceptions and controversies surrounding this fundamental concept, fostering a deeper understanding of its implications for our understanding of the natural world and our place within it.
Definition of Evolution and Natural Selection
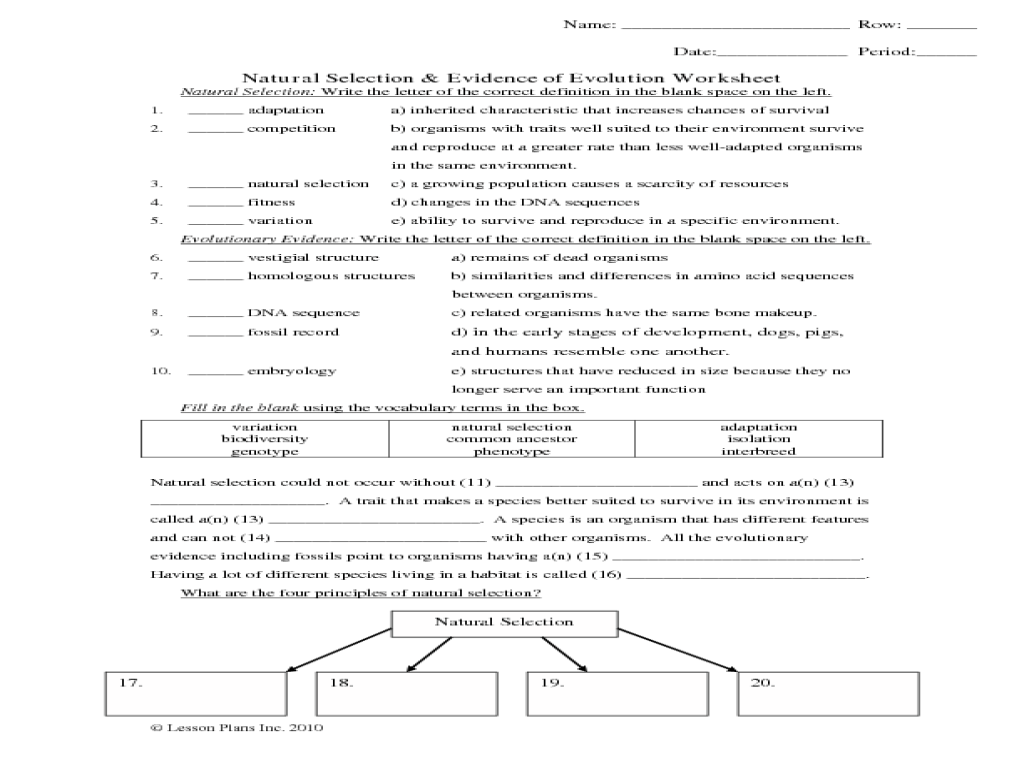
Evolution refers to the gradual change in species over time, resulting in the formation of new species. Natural selection, a fundamental mechanism driving evolution, describes the process where organisms with traits that provide an advantage in their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring.
Key Principles of Evolution and Natural Selection: Evolution And Natural Selection Worksheet
Role of Genetic Variation in Evolution
Evolution relies on genetic variation, the differences in traits among individuals within a species. This variation arises from mutations, gene flow, genetic recombination, and other genetic processes.
Influence of Environmental Pressures on Natural Selection
Natural selection operates under the influence of environmental pressures. Environmental factors, such as predation, competition for resources, and climate change, shape which traits are advantageous and contribute to survival and reproduction.
Examples of Natural Selection Leading to Adaptation
Natural selection has led to numerous adaptations in species, enabling them to thrive in their respective environments. Examples include the development of camouflage in prey species to avoid predators, the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and the formation of long necks in giraffes to reach high-growing leaves.
Evidence Supporting Evolution and Natural Selection
Fossil Record
The fossil record provides a historical record of extinct species, showcasing the gradual changes in species over time. Transitional fossils, such as Archaeopteryx, exhibit characteristics of both ancestral and modern species, supporting the theory of evolution.
Comparative Anatomy and Homologous Structures
Comparative anatomy examines the similarities and differences in body structures across species. Homologous structures, such as the forelimbs of humans and whales, share a common evolutionary origin despite serving different functions.
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology provides evidence for evolution by comparing DNA sequences. Closely related species share more similar DNA sequences, supporting the concept of common ancestry.
Misconceptions and Controversies Surrounding Evolution and Natural Selection
Common Misconceptions about Evolution, Evolution and natural selection worksheet
Evolution is not a linear progression from “lower” to “higher” forms. Instead, it is a branching process that leads to the diversity of life.
Debate over Intelligent Design
Intelligent design posits that certain features of the natural world cannot be explained by natural processes alone and require the intervention of an intelligent designer. This view remains controversial and lacks scientific support.
Evolution and Societal Issues
Evolution and natural selection can be applied to address societal issues. For example, understanding antibiotic resistance helps develop strategies to combat the spread of infectious diseases.
General Inquiries
What is the difference between evolution and natural selection?
Evolution refers to the gradual change in species over time, while natural selection is the process by which organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, driving evolutionary change.
How does genetic variation contribute to evolution?
Genetic variation provides the raw material for evolution, as it introduces differences among individuals within a population, allowing for natural selection to act upon these variations.
What are some examples of natural selection in action?
Natural selection has led to adaptations such as antibiotic resistance in bacteria, camouflage in animals, and the development of specialized structures like the giraffe’s long neck for reaching high leaves.