Most analog addressable systems operate on a voltage loop, which is a type of control system that uses feedback to maintain a desired voltage level. The voltage loop is used to control the output of a power supply or other device by comparing the actual output voltage to a reference voltage and adjusting the output voltage accordingly.
Voltage loops are used in a wide variety of applications, including power supplies, audio amplifiers, and motor controllers. In a power supply, the voltage loop is used to regulate the output voltage to a specific level, regardless of changes in the input voltage or load current.
In an audio amplifier, the voltage loop is used to control the output voltage so that it follows the input signal. In a motor controller, the voltage loop is used to control the speed of the motor by adjusting the voltage applied to the motor.
System Architecture
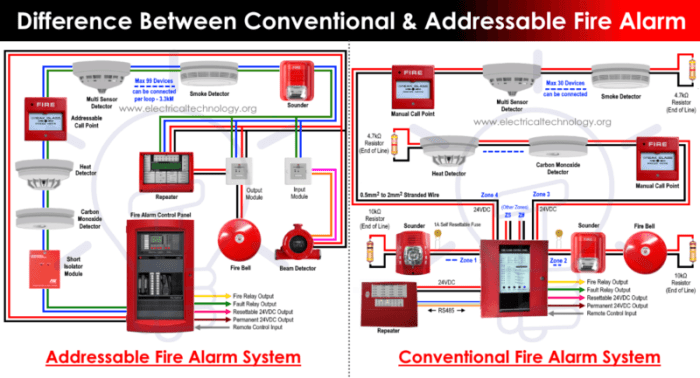
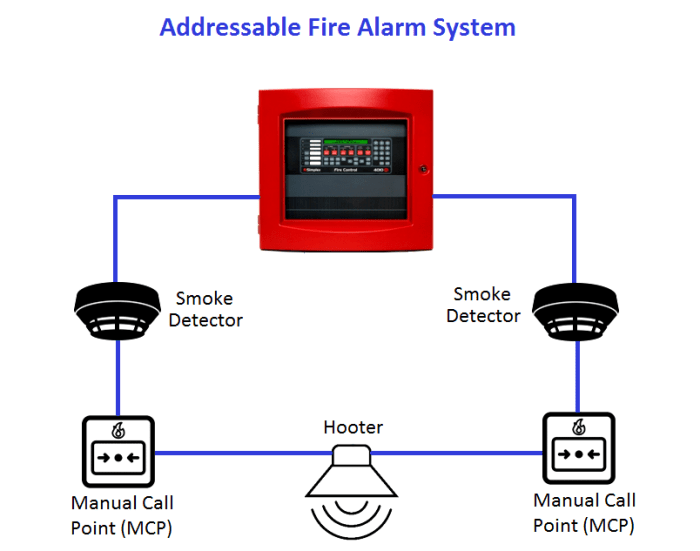
Analog addressable systems typically follow a distributed architecture, consisting of a central control panel, loop controllers, and addressable devices.
The central control panel is the brains of the system, managing communication and monitoring the status of all devices. Loop controllers connect to the control panel and provide power and communication to the addressable devices within their respective loops.
Addressable devices include smoke detectors, heat detectors, manual call points, and other input/output devices. Each device has a unique address that allows the control panel to identify and communicate with it.
System Architecture Diagram, Most analog addressable systems operate on a
A simplified diagram of an analog addressable system architecture:
- Central control panel
- Loop controllers
- Addressable devices (e.g., smoke detectors, heat detectors, manual call points)
Addressing Schemes: Most Analog Addressable Systems Operate On A
Analog addressable systems use various addressing schemes to identify and locate individual devices on the loop.
Rotary Addressing
Rotary addressing uses a rotary switch on the device to set its address. The address is typically a number between 1 and 255.
Binary Addressing
Binary addressing uses a series of DIP switches on the device to set its address. Each switch represents a bit in the binary address, allowing for a wider range of addresses.
Auto-Addressing
Auto-addressing allows devices to automatically assign themselves an address when connected to the loop. This simplifies installation and maintenance.
Communication Protocols
Analog addressable systems use various communication protocols to transmit data between devices.
Analog Loop Protocol (ALP)
ALP is a widely used protocol for analog addressable systems. It uses frequency-shift keying (FSK) to modulate data onto the loop current.
Digital Loop Protocol (DLP)
DLP is a newer protocol that uses digital modulation to transmit data over the loop. DLP provides higher data rates and improved noise immunity compared to ALP.
Signal Processing
Analog addressable systems use various signal processing techniques to modulate and demodulate data.
Modulation
Modulation is the process of encoding data onto a carrier signal. Analog addressable systems typically use frequency-shift keying (FSK) or amplitude-shift keying (ASK) to modulate data onto the loop current.
Demodulation
Demodulation is the process of recovering data from a modulated signal. Analog addressable systems use demodulators to extract the data from the loop current.
Applications

Analog addressable systems are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Fire alarm systems
- Security systems
- Building automation systems
- Industrial control systems
Advantages
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Reliability
- Cost-effectiveness
Disadvantages
- Limited data bandwidth
- Susceptibility to noise and interference
- Complexity of installation and maintenance
Answers to Common Questions
What is a voltage loop?
A voltage loop is a type of control system that uses feedback to maintain a desired voltage level.
What are the advantages of using a voltage loop?
Voltage loops are simple to implement and provide good performance.
What are the disadvantages of using a voltage loop?
Voltage loops can be sensitive to noise and can be slow to respond to changes in the input voltage or load current.