Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of chemistry empirical formula worksheet answers, where we unravel the intricacies of this fundamental concept. This guide will equip you with a thorough understanding of empirical formulas, empowering you to navigate the intricacies of chemical composition with confidence.
Delving into the essence of empirical formulas, we explore their significance in chemistry, enabling you to decipher the language of chemical compounds. Through practical examples and step-by-step guidance, this comprehensive guide empowers you to master the art of determining empirical formulas, ensuring accuracy and precision in your chemical endeavors.
1. Introduction

Chemistry is the study of the composition, structure, properties, and change of matter. It is a vast and complex field that has applications in many different areas, including medicine, engineering, and materials science.
Empirical formulas are a simplified way of representing the composition of a compound. They show the relative proportions of the different atoms in a compound, but they do not indicate the arrangement of the atoms. Empirical formulas are important because they can be used to identify compounds, calculate their molecular weights, and predict their properties.
2. Understanding Empirical Formula Worksheets
Empirical formula worksheets are a tool that can be used to help students determine the empirical formula of a compound. These worksheets typically provide a step-by-step guide to the process, and they can be a valuable resource for students who are struggling with this concept.
To use an empirical formula worksheet, students will need to know the mass of each element in the compound. This information can be obtained from a variety of sources, such as a periodic table or a chemical database. Once the student has the mass of each element, they can use the worksheet to calculate the empirical formula.
3. Steps to Determine Empirical Formula: Chemistry Empirical Formula Worksheet Answers
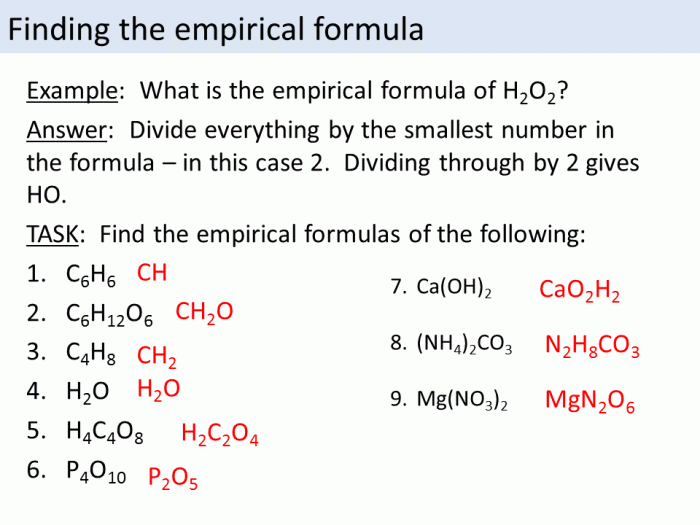
The steps involved in determining the empirical formula of a compound using a worksheet are as follows:
- Convert the mass of each element to moles.
- Divide the number of moles of each element by the smallest number of moles.
- Simplify the resulting ratios to whole numbers.
- Write the empirical formula using the simplified ratios.
For example, if a compound has 12.01 g of carbon, 2.016 g of hydrogen, and 32.00 g of oxygen, the empirical formula would be CH 2O.
4. Common Errors and Troubleshooting
There are a number of common errors that students make when using empirical formula worksheets. These errors include:
- Using the wrong units.
- Not converting the mass of each element to moles.
- Not dividing the number of moles of each element by the smallest number of moles.
- Not simplifying the resulting ratios to whole numbers.
If you are having trouble determining the empirical formula of a compound, it is important to check your work for these common errors.
5. Applications of Empirical Formulas

Empirical formulas have a number of practical applications in chemistry. These applications include:
- Identifying compounds.
- Calculating molecular weights.
- Predicting properties.
For example, the empirical formula of a compound can be used to identify the compound by comparing it to a database of known compounds. The empirical formula can also be used to calculate the molecular weight of the compound, which is important for determining its density and other properties.
Top FAQs
What is the purpose of an empirical formula worksheet?
Empirical formula worksheets provide a structured approach to determine the empirical formula of a compound, which represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements present in the compound.
How do I use an empirical formula worksheet?
Empirical formula worksheets guide you through a series of steps, including calculating the mass percentages of each element, determining the mole ratio, and simplifying the ratio to obtain the empirical formula.
What are common errors to avoid when using empirical formula worksheets?
Common errors include incorrect calculation of mass percentages, neglecting to simplify the mole ratio to its simplest whole-number form, and assuming the empirical formula is the same as the molecular formula.